
This is my first time to participate in Google Search Central event, and the whole process was great, including the entrance, photos, meals, Q&A, the overall rhythm was very well controlled, why would I organize my notes in English? The first reason is that this event is conducted in English, and the second reason is that I want to strengthen my English expression, so maybe this is an opportunity for me.
Well, without further words, here are the topics for this event, I’ll organize some of the main content, some of the less important content may be briefly explained (with documentation attached), and of course I’ll add my own insights.
How Search works: the longer version, Cherry Prommawin
The Google search engine works in 3 main processes:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Serving
But according to Cherry’s explanation, it can actually be subdivided into five.
- Discovering, trillions of URLs on the Internet
- Crawling, Google’s stage of collecting web pages
- Redering, analyzing the appearance and functionality of a page
- Indexing, organizing and storing page information
- Serving (Ranking), determining the relevance and sequence of pages and presenting them to users
For more details, you can browse this version
About quality and updates: the longer version, Gary Illyes & Vince Yue
This topic talks about why Google releases so many updates and how it judges the quality of a page.
Google spends a huge amount of money every year to deal with spam sites/content, especially in the last two years is the development of AI tools, internet spam content is growing exponentially. Here image shows that Google will detect 40 billion spam pages per day in 2021.

In addition to dealing with spammy content, the growing content in the Internet, and changing search behavior, Google has been updated several times to better meet the searchers’ search intent.
Here Gary shares three directions on content:

Here Vince explains how webmasters can create quality content in these key dimensions,

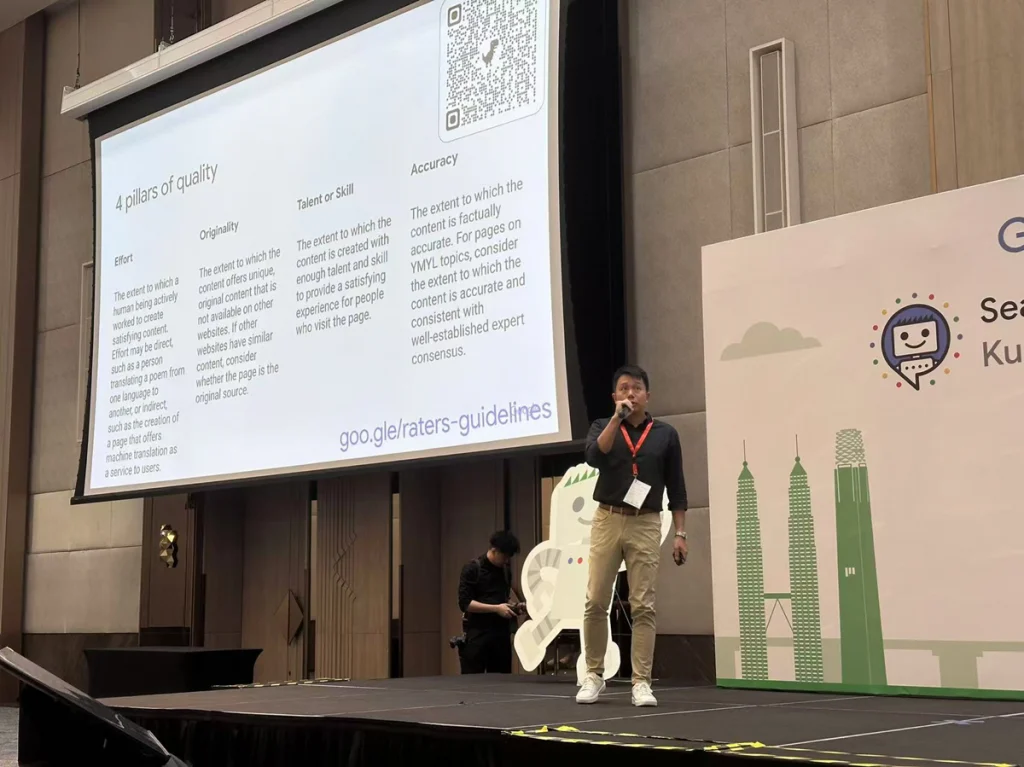
He also cites the “4 Pillars of Quality” of the Search Quality Rater Guidelines,

AI and Search: the 2024 version, Gary Illyes
Gary first talked about the definition and relationship between AI, ML, and LLM;




Then he talked about how Google search utilizes these three tools, and finally led to the AI Overview.




When explaining this, Gary demonstrated a local Malaysian song – Rasa Sayang, he sang the first line, the next line will be sung to the Malaysian participants, he sang through this process to analogize the AI, that is, the AI will analyze the current scene, and automatically guess what you need next, it may be text, pictures, video, etc., this is because AI learns from a lot of data through ML, which makes Google “smarter” and knows exactly what related content the user will be interested in, and then returns the related high-quality web pages or answers to the user.
In this section Gary also inserted a question about AI content and human written content, the question was
“Can Google distinguish between ai and human written content?”
Gary roughly answered that Google can, but Google will not go to spend energy in this area, as long as the content meets the quality standards, it is Google’s favor.
This part of the answer is very official and expresses Google’s position, so Gary’s attitude is consistent with this document.
More AI content can also be learned here,
- https://ai.google/static/documents/google-about-generative-ai.pdf
Analysing traffic drop using Search Console, Aaseesh Marina
More on this chapter can be found at
Aaseesh also synchronizes 5 tips for checking website traffic anomalies,

Your site and features on Search, Cassie Chan
Cassie covered this chapter very quickly, finishing the chapter in about 10 minutes, the main point is that SERPs are not the same as they were 10 or 20 years ago, they have evolved from a simple 10 bule link to a diverse range of videos, images, knowledge panels, curated summaries, PAA, etc., which is all attributed to the change in human search behavior and the diversification of content.
SEO for video, Cassie Chan
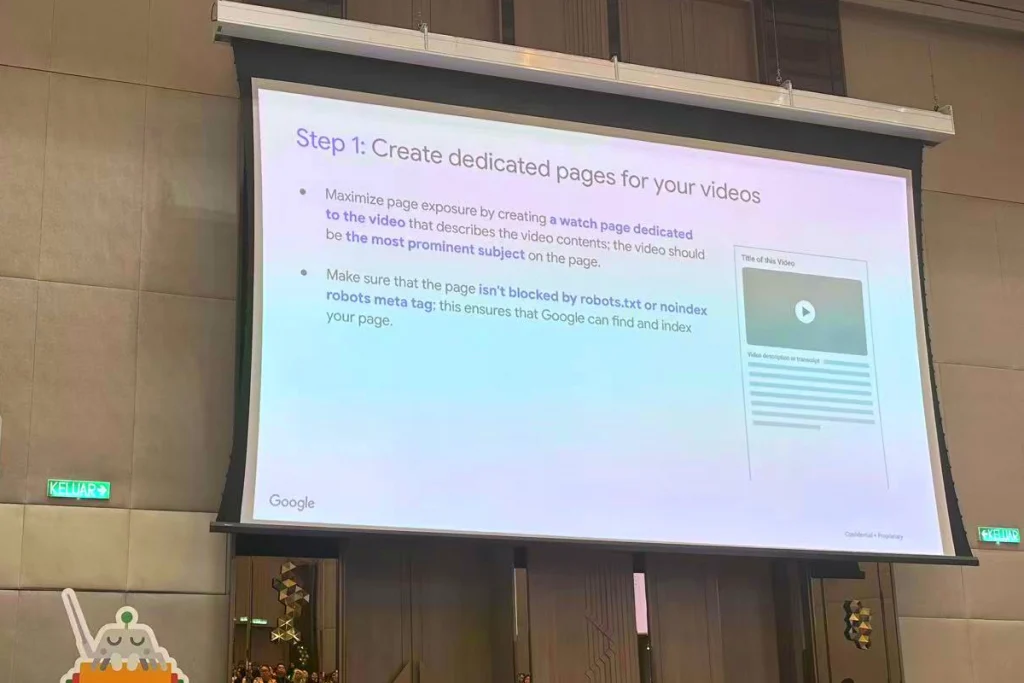

Video traffic accounts for more than 80% of the Internet traffic, here some people ask what region, Cassie answered is the world, it can be seen that the video content is more favored by the searchers, but it depends on the search needs of the searchers, for SEO for video, you can refer to the
Rich results for e-commerce sites, Risa de Sagun
In this topic, Risa talked about the presentation of the Google Shopping interface and the benefits of GMCN for every online or physical merchant, as well as the new feature of GMCN, Product Studio, which is a tool that can help you make changes to the main image of your products, a feature that I have tested in the last couple of months and it’s very interesting.
Here I found the related documents, you can learn about it if you are interested,
SEO Mythbusting, Cherry Prommawin & Gary Illyes
I only recorded some key questions in this section, I didn’t record the part like “SEO is dead?”, as Gary answered that SEO is dead every year,~XD.
Q: New domain/business cannot outrank on established domain/business?
A: Incorrect, it’s more about the quality of the content, the quality of the site.
Q: I need buy backlinks?
A: Kinda waste money.
Q: Focusing on my website is better than focusing on social media
A: It depends on your users!
Q: It is safe to ignore random low quality/toxic links pointing to your site
A: Sure.
Q: Google prefers subdomains to subdirectories
A: We don’t have preference there.
Internationalisation and localisation, Cherry Prommawin
This section is very detailed and many notes, which is why Google is globalizing, but most of the chapter revolves around the following document.


A couple of important points that Cherry makes in the form of questions.
Q: Will Google use hredlang or HTML lang attributes to judge web language?
A: No. Google looks at the language of the content when indexing. hredlang is used to make it easier to determine, and is still a strong signal to Google, for example, to determine if it’s Malaysian English or some other English language through hreflang.
Q: Does Google use the language of the URL fragment page?
A: No. Google will look at the language of the content. So if a web page has multiple languages, it will be confusing for both users and Google.
Q: Would it be slightly better to have different ccTLDs for different country versions of the site?
A: Yes. But it is not necessarily required that you use CCTLD.
Q: Is it possible to use machine translation?
A: Yes, but we have to consider the quality of the translation and whether it is suitable for users’ browsing habits. It is recommended that the translation should be reviewed by human beings to understand the culture of the users before publishing.

The whole event was a great experience for me, and I certainly look forward to the next year, where you can meet a lot of interesting people and learn about their business, work habits and lifestyles. For doing business overseas, as with SEO, you can’t be stuck in your ways, you have to get out there and learn new models.